Screening for Characteristic Genes of Different Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndromes of Psoriasis Vulgaris: A Study Based on Bioinformatics and Machine Learning
-
摘要:目的
通过生物信息学和机器学习筛选寻常型银屑病(psoriasis vulgaris, PV)血热证(blood-heat syndrome, BHS)、血瘀证(blood stasis syndrome, BSS)及血燥证(blood-dryness syndrome, BDS)的重要特征基因,为不同中医证型PV的临床诊疗提供科学依据。
方法从基因表达数据库(Gene Expression Omnibus, GEO)下载GSE192867数据集,利用limma包筛选患者与健康人群的PV、BHS、BSS及BDS差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes, DEGs),并进行KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)通路富集分析。将PV、BHS、BSS及BDS筛选出的DEGs分别取交集,获取不同的特征基因。利用支持向量机(support vector machine, SVM)和随机森林(random forest, RF)两种算法中效能最优的方法对特征基因进行分析,将排序前5的基因作为重要特征基因,并利用pROC包绘制重要特征基因的受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)曲线,计算曲线下面积(area under the curve, AUC),评价其诊断效能。
结果筛选出与PV、BHS、BSS以及BDS相关的DEGs数量分别为
7699 个、7291 个、7654 个和6578 个。KEGG富集分析主要集中在Janus激酶(Janus kinase,JAK)/信号转导与转录激活因子(signal transducer and activator of transcription, STAT)、环磷酸腺苷(cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK),以及细胞凋亡等通路。通过机器学习共筛选出13个重要特征基因,其中凝集素(malectin, MLEC)、TUB样蛋白3(TUB like protein 3, TULP3)、含SET域9(SET domain containing 9, SETD9)、核膜整合膜蛋白2(nuclear envelope integral membrane protein 2, NEMP2)和BTG抗增殖因子3(BTG anti-proliferation factor 3, BTG3)是BHS的重要特征基因,双特异性磷酸酶15(dual specificity phosphatase 15, DUSP15)、C1q与肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白7(C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 7, C1QTNF7)、溶质载体家族12成员5(solute carrier family 12 member 5, SLC12A5)、含三联基元63(tripartite motif containing 63, TRIM63)和泛素相关蛋白样因子1(ubiquitin associated protein 1 like, UBAP1L)是BSS的重要特征基因,重组小鼠蛋白(recombinant mouse protein, RRNAD1)、GTP酶激活蛋白ASAP3蛋白(ASAP3 protein, ASAP3 )和人肌间蛋白2(human myomesin 2, MYOM2)是BDS的重要特征基因,且PV不同证型的特征基因ROC曲线均表现出较高诊断效能。结论PV不同证型的特征基因存在显著差异,其可能成为潜在的诊断PV中医证型的生物标志物。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo screen for the key characteristic genes of the psoriasis vulgaris (PV) patients with different Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) syndromes, including blood-heat syndrome (BHS), blood stasis syndrome (BSS), and blood-dryness syndrome (BDS), through bioinformatics and machine learning and to provide a scientific basis for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of PV of different TCM syndrome types.
MethodsThe GSE192867 dataset was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). The limma package was used to screen for the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of PV, BHS, BSS, and BDS in PV patients and healthy populations. In addition, KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genes) pathway enrichment analysis was performed. The DEGs associated with PV, BHS, BSS, and BDS were identified in the screening and were intersected separately to obtain differentially characterized genes. Out of two algorithms, the support vector machine (SVM) and random forest (RF), the one that produced the optimal performance was used to analyze the characteristic genes and the top 5 genes were identified as the key characteristic genes. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the key characteristic genes were plotted by using the pROC package, the area under curve (AUC) was calculated, and the diagnostic performance was evaluated, accordingly.
ResultsThe numbers of DEGs associated with PV, BHS, BSS, and BDS were
7699 ,7291 ,7654 , and6578 , respectively. KEGG enrichment analysis was focused on Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT), cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), apoptosis, and other pathways. A total of 13 key characteristic genes were identified in the screening by machine learning. Among the 13 key characteristic genes, malectin (MLEC), TUB like protein 3 (TULP3), SET domain containing 9 (SETD9), nuclear envelope integral membrane protein 2 (NEMP2), and BTG anti-proliferation factor 3 (BTG3) were the key characteristic genes of BHS; phosphatase 15 (DUSP15), C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 7 (C1QTNF7), solute carrier family 12 member 5 (SLC12A5), tripartite motif containing 63 (TRIM63), and ubiquitin associated protein 1 like (UBAP1L) were the key characteristic genes of BSS; recombinant mouse protein (RRNAD1), GTPase-activating protein ASAP3 Protein (ASAP3), and human myomesin 2 (MYOM2) were the key characteristic genes of BDS. Moreover, all of them showed high diagnostic efficacy.ConclusionThere are significant differences in the characteristic genes of different PV syndromes and they may be potential biomarkers for diagnosing TCM syndromes of PV.
-
Keywords:
- Psoriasis /
- Traditional Chinese Medicine /
- Syndrome /
- Bioinformatics /
- Machine learning /
- Biomarkers
-
银屑病属于临床中常见的慢性炎症性皮肤病,可分为寻常型、关节型、脓疱型、红皮型等,其中寻常型银屑病(psoriasis vulgaris, PV)占总发病人数的90%以上[1]。中医又将PV分为血热证(blood-heat syndrome, BHS)、血瘀证(blood stasis syndrome, BSS)及血燥证(blood-dryness syndrome, BDS),并且通过中医中药辨证治疗效果良好,获得临床广泛应用[2]。目前,虽然有不少研究人员对PV不同中医证型的相关分子和机制进行了研究[3-5],但其机制并不完全清楚。因此,挖掘BHS、BSS、BDS的潜在标志物对于PV的临床诊断、治疗以及病理机制的研究至关重要。
近年来,生物信息学和机器学习在进行寻找疾病的关键基因,筛选生物标记物方面展现出巨大的潜力,也成为PV生物标志物、治疗靶点预测的重要手段[6-9]。本研究拟利用生物信息学方法从基因表达数据库(Gene Expression Omnibus, GEO)获取PV患者相关基因矩阵,并用机器学习算法对BHS、BSS、BDS的重要特征基因进行筛选,初步探索其潜在的生物标记物,以期为银屑病临床辨证诊疗提供新的参考。
1. 材料及方法
1.1 数据来源与预处理
通过GEO数据库(http://www.ncbi. nlm.nih.gov/geo/)下载GSE192867数据集。该数据集中有10例来自健康人群,有62例PV患者(其中BHS患者16例、BSS患者23例、BDS患者23例)。在数据集中,用Affymetrix Human Clariom D Assay检测健康人群和PV患者外周血单核细胞转录组的表达。提取数据集中的健康人群和PV患者的数据保存为“PV.txt”文件;然后,分别提取BHS、BSS和BDS的数据,再与健康人群的数据逐一合并,分别保存为“BHS.txt”文件、“BSS.txt”文件和“BDS.txt”文件。利用Perl脚本根据数据集的平台文件(GPL23126)将其探针矩阵转化为基因矩阵,基因对应多个探针者则利用avereps函数对其取均值,并用normalizeBetweenArrays函数进行矫正。
1.2 筛选差异表达基因
利用limma包分别对“PV.txt”、“BHS.txt”、“BSS.txt”和“BDS.txt”文件进行差异分析[10]。以|log2(fold change, FC)|>3,P<0.05为标准筛选差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes, DEGs),并绘制火山图。
1.3 功能富集分析
利用org.Hs.eg.db、clusterProfiler、enrichplot等R语言包对筛选的DEGs进行KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)通路富集分析,并绘制气泡图。
1.4 不同中医证型重要特征基因的筛选
将“PV.txt”、“BHS.txt”、“BSS.txt”和“BDS.txt”文件数据筛选的DEGs分别取交集,并绘制维恩图。去除其中任意一种证型DEGs与其余证型DEGs重合部分,剩余基因与PV的DEGs取交集后所得基因定义为该种证型的特征基因。如BHS的特征基因是在BHS的DEGs与PV的DEGs的交集基因中,这些基因既不属于BSS,也不属于BDS的交集基因。
1.5 机器学习算法识别不同中医证型的重要特征基因
筛选出GSE192867数据集中不同中医证型特征基因的相关表达数据,分别构建支持向量机(support vector machine, SVM)和随机森林(random forest, RF)模型,并利用“dalx”包对2种模型进行分析评价,绘制残差分布,残差最小者即最佳模型,将最佳模型筛选出来的重要性排序前5的基因作为该中医证型的重要特征基因。
1.6 不同中医证型重要特征基因的评价
提取不同中医证型重要特征基因在各样本中的表达量,绘制柱形图并对其组间差异情况进行可视化;然后,通过pROC包对关键基因受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)进行曲线绘制,计算曲线下面积(area under the curve, AUC)值,对重要特征基因的诊断效能进行评价。
2. 结果
2.1 DEGs的筛选
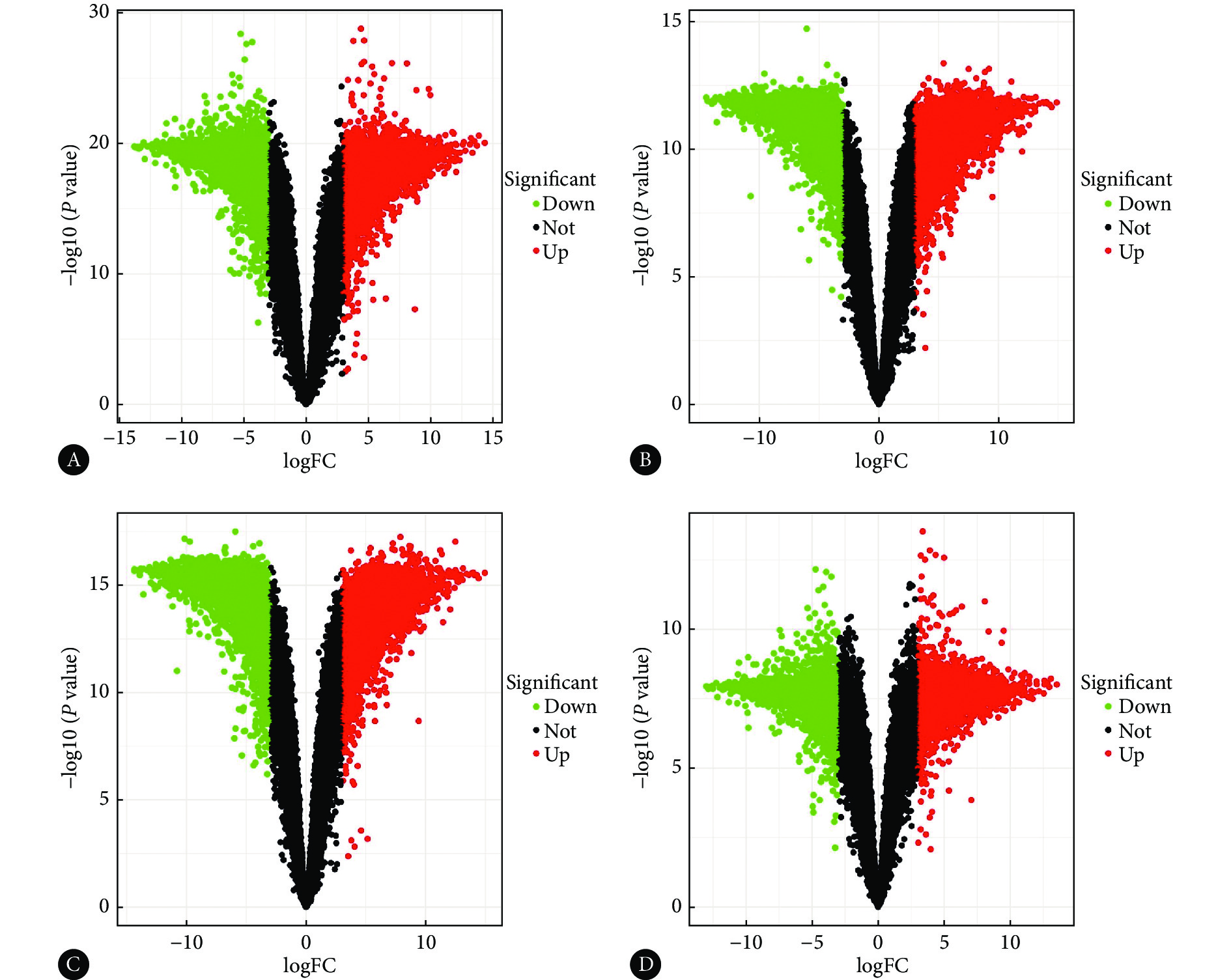
差异分析结果显示,“PV.txt”共筛选出
7699 个与PV相关的DEGs(图1A);“BHS.txt”共筛选出7291 个与BHS相关的DEGs(图1B);“BSS.txt”共筛选出7654 个与BSS相关的DEGs(图1C);“BDS.txt”共筛选出6578 个与BDS相关的DEGs(图1D)。![]() 图 1 DEGs火山图Figure 1. The volcano map of DEGsA, "PV.txt" file; B, "BHS.txt" file; C: "BSS.txt" file ; D, "BDS.txt" file. Each dot represents a gene, with the green dots representing down-regulated DEGs, the gray dots representing genes not differentially expressed, and the red dots representing up-regulated DEGs.
图 1 DEGs火山图Figure 1. The volcano map of DEGsA, "PV.txt" file; B, "BHS.txt" file; C: "BSS.txt" file ; D, "BDS.txt" file. Each dot represents a gene, with the green dots representing down-regulated DEGs, the gray dots representing genes not differentially expressed, and the red dots representing up-regulated DEGs.2.2 DEGs的KEGG富集分析
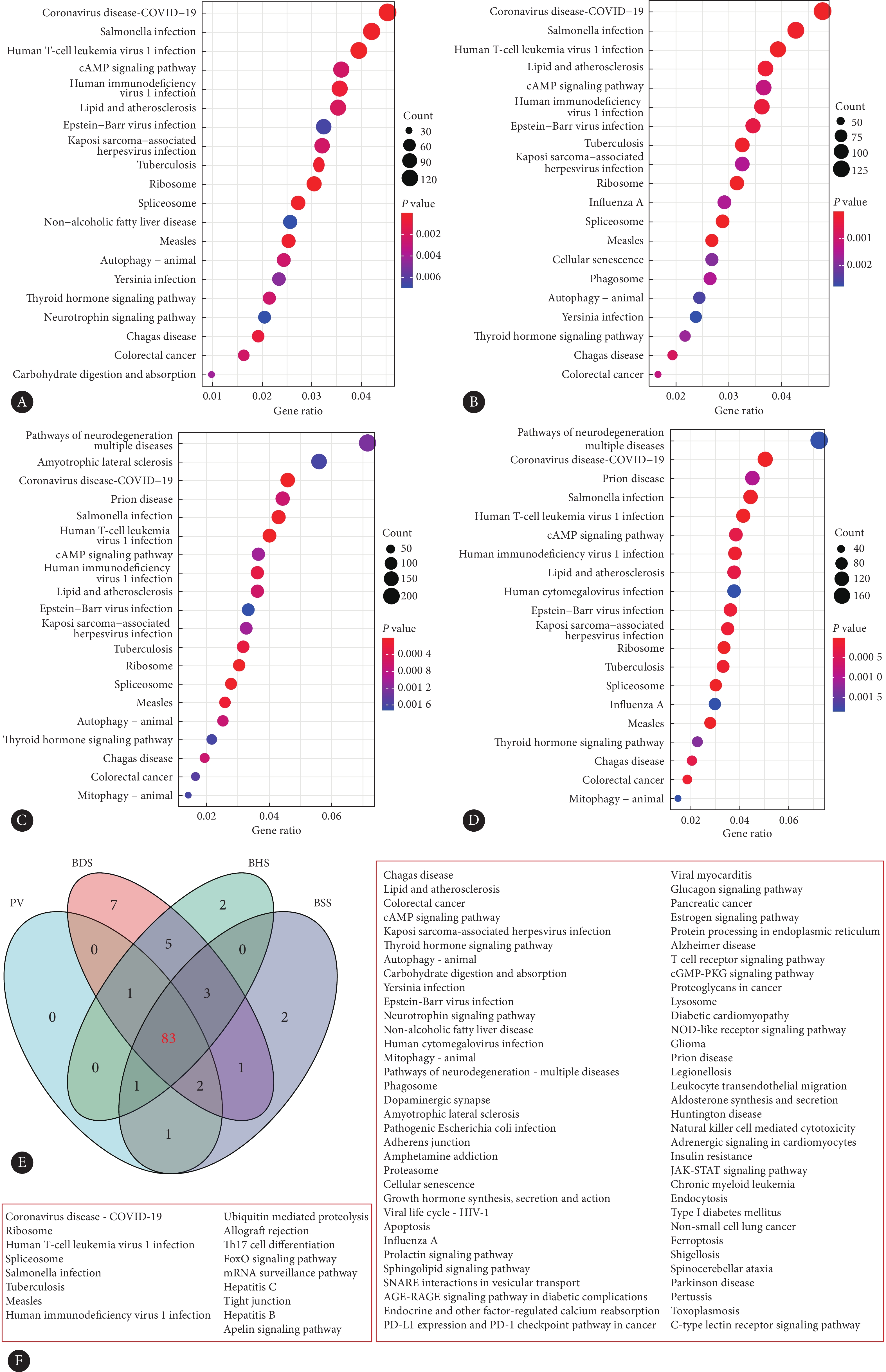
KEGG分析结果显示,依据P值<0.05为显著通路筛选的标准,PV相关DEGs有88条信号通路,涉及环磷酸腺苷(cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP)信号通路、自噬等(图2A);BHS相关DEGs有95条信号通路,包括核糖体、吞噬体等(图2B);BSS相关DEGs有93条信号通路,涉及cAMP信号通路、线粒体自噬等(图2C);BDS相关DEGs有102条信号通路,包括cAMP信号通路、剪切体等(图2D)。所有富集出的通路取交集后,共有83条共同通路(图2E、2F)。
![]() 图 2 DEGs功能富集分析Figure 2. DEGs functional enrichment analysis resultsA, Bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of PV-related DEGs; B, bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of BHS-related DEGs; C, bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of BSS related DEGs; D, bubble diagram of KEGG enrichment analysis of BDS-related DEGs; E, Venn diagram of KEGG pathways for all DEGs; F, the intersection KEGG pathway of all DEGs.
图 2 DEGs功能富集分析Figure 2. DEGs functional enrichment analysis resultsA, Bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of PV-related DEGs; B, bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of BHS-related DEGs; C, bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of BSS related DEGs; D, bubble diagram of KEGG enrichment analysis of BDS-related DEGs; E, Venn diagram of KEGG pathways for all DEGs; F, the intersection KEGG pathway of all DEGs.2.3 生物信息学筛选不同中医证型重要特征基因
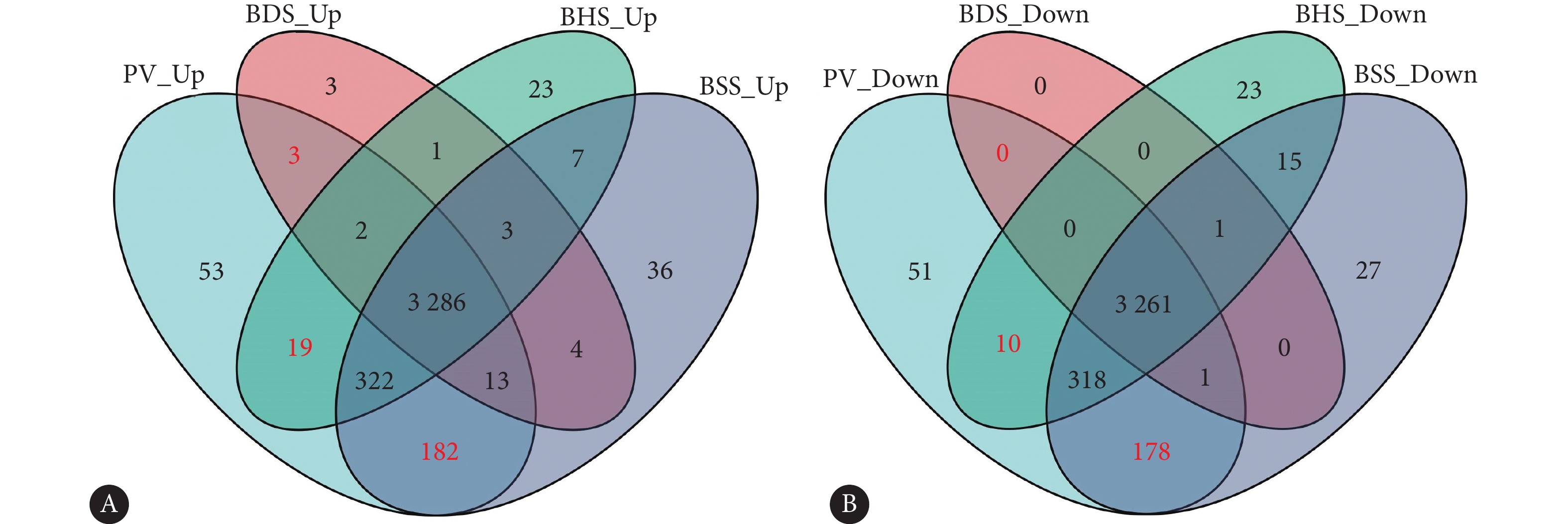
BHS共获得29个特征基因;BSS共获得360个特征基因;BDS共获得3个特征基因。本研究筛选出的中医证型特征基因仅为本中医证型特有的基因,鉴于BDS的特征基因较少,故将BDS筛选出的3个上调的特征基因认定为BDS的重要特征基因(图3)。
2.4 机器学习算法识别不同中医证型重要特征基因
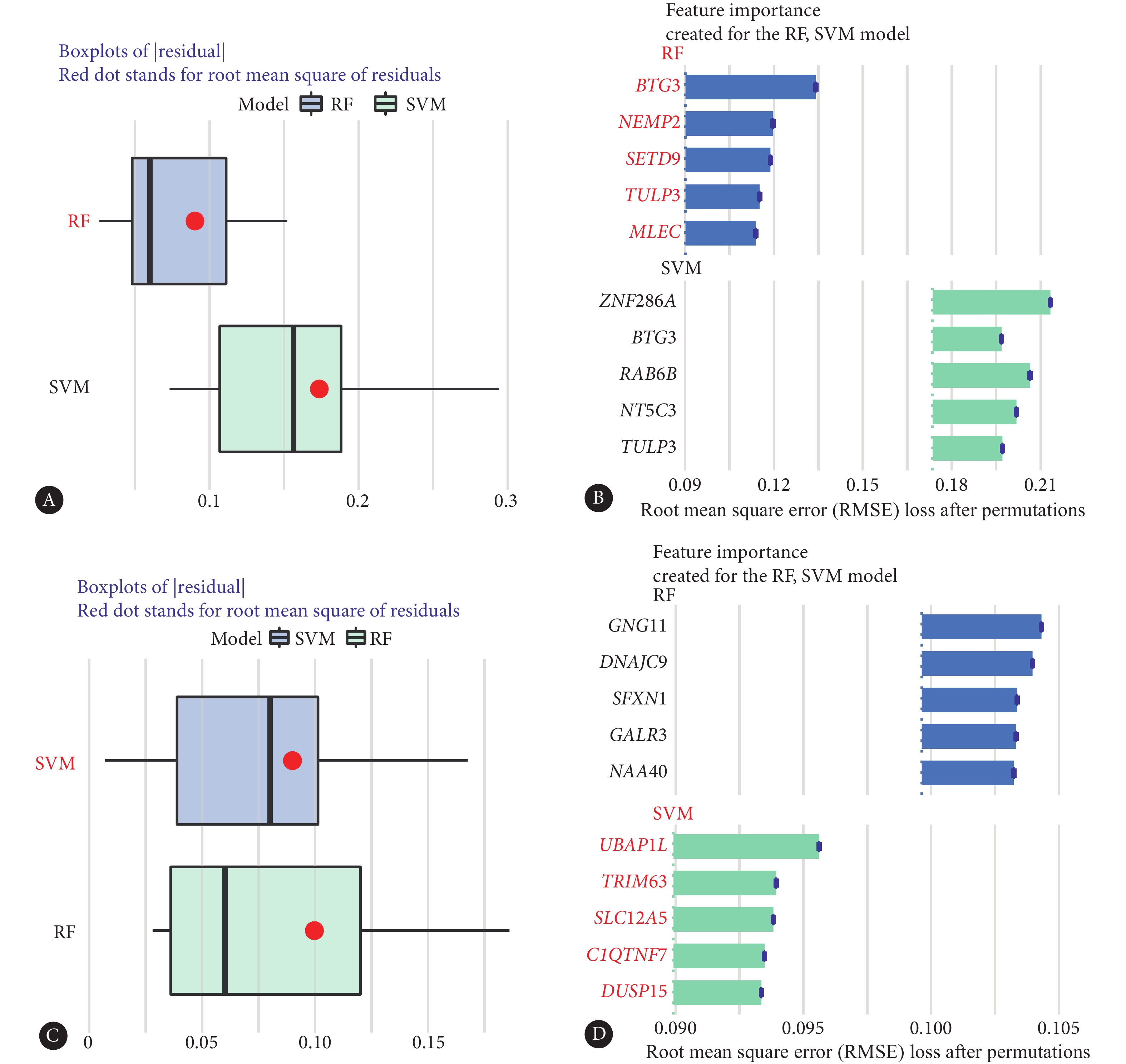
依据RF模型的筛选结果,在29个BHS特征基因中,凝集素(malectin, MLEC)、TUB样蛋白3(TUB like protein 3, TULP3)、含SET域9(SET domain containing 9, SETD9)、核膜整合膜蛋白2(nuclear envelope integral membrane protein 2, NEMP2)、BTG抗增殖因子3(BTG anti-proliferation factor 3, BTG3)为重要特征基因(图4A、4B)。依据SVM模型的筛选结果,在360个BSS特征基因中,双特异性磷酸酶15(dual specificity phosphatase 15, DUSP15)、C1q与肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白7(C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 7, C1QTNF7)、溶质载体家族12成员5(solute carrier family 12 member 5, SLC12A5)、含三联基元63(tripartite motif containing 63, TRIM63)、泛素相关蛋白样因子1(ubiquitin associated protein 1 like, UBAP1L)为重要特征基因(图4C、4D)。
![]() 图 4 机器学习算法筛选不同中医证型的重要特征基因Figure 4. The key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome types were screened by machine learning algorithmA, Box plot of BHS sample residuals, with the red dots representing the root mean square of residuals; B, importance ranking of BHS characteristic genes in the two models; C, box plot of BSS sample residuals, with the red dots representing the root mean square of residuals; D, the importance ranking of BSS characteristic genes in the two models.
图 4 机器学习算法筛选不同中医证型的重要特征基因Figure 4. The key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome types were screened by machine learning algorithmA, Box plot of BHS sample residuals, with the red dots representing the root mean square of residuals; B, importance ranking of BHS characteristic genes in the two models; C, box plot of BSS sample residuals, with the red dots representing the root mean square of residuals; D, the importance ranking of BSS characteristic genes in the two models.2.5 不同中医证型重要特征基因的评价
图5A为重要特征基因的染色体位置。不同中医证型重要特征基因的AUC值均大于0.7,并且多数均大于0.9,表明具有良好的诊断准确性(图5B、5C)。其中BHS和BSS的AUC值均大于0.9(图5D、5E),BDS的AUC值均大于0.8(图5F),表现出良好诊断效能。此外,所有重要特征基因在自身证型数据中的表达趋势与“PV.txt”文件数据中呈现的表达趋势基本一致(图6A~6D)。
![]() 图 5 不同中医证型重要特征基因诊断效能的评价Figure 5. Evaluation of the diagnostic efficacy of key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome typesA, Chromosomal location of key characteristic genes; B-C, ROC curve of key characteristic genes in the "PV.txt" file; D, ROC curve of key BHS characteristic genes in "BHS. txt" file; E, ROC curve of key BSS characteristic genes in the "BSS.txt" file; F, ROC curve of BDS key characteristic genes in "BDS.txt" file.
图 5 不同中医证型重要特征基因诊断效能的评价Figure 5. Evaluation of the diagnostic efficacy of key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome typesA, Chromosomal location of key characteristic genes; B-C, ROC curve of key characteristic genes in the "PV.txt" file; D, ROC curve of key BHS characteristic genes in "BHS. txt" file; E, ROC curve of key BSS characteristic genes in the "BSS.txt" file; F, ROC curve of BDS key characteristic genes in "BDS.txt" file.![]() 图 6 重要特征基因的表达趋势Figure 6. Expression trends of key characteristic genesA, Box diagram of the expression of key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome types in the "PV.txt" file; B, box diagram of the expression of BHS key characteristic genes in the "Bhs.txt" file; C, box diagram of the expression of BSS key characteristic genes in the "BSS.txt" file; D, box diagram of the expression of BDS key characteristic genes in the file "BDS.txt". * P<0.05, *** P<0.001.
图 6 重要特征基因的表达趋势Figure 6. Expression trends of key characteristic genesA, Box diagram of the expression of key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome types in the "PV.txt" file; B, box diagram of the expression of BHS key characteristic genes in the "Bhs.txt" file; C, box diagram of the expression of BSS key characteristic genes in the "BSS.txt" file; D, box diagram of the expression of BDS key characteristic genes in the file "BDS.txt". * P<0.05, *** P<0.001.3. 讨论
PV发病机制复杂,其病因尚未完全阐明。尽管遗传、感染、代谢、外伤、季节、药物、压力、吸烟和饮酒等因素都是PV的发病诱因[11],但识别其高危分子标志物及发病机制仍是一个难题。因此,探索PV分子发病机制和诊断标志物具有重要意义。
辨证论治是中医学基本原则,中医学家司外揣内,审时度势,四诊合参,将PV分为BHS、BSS、BDS三证,治疗准确,优势显著[2, 12-13]。但传统辨证受个体差异、思维方式等因素的影响呈现出复杂性、模糊性,通过筛选各证型重要特征基因可提升辨证准确性与适用度,更好地指导临床辨证施治。
本研究通过对GSE192867数据集进行差异分析,筛选出
7699 个与PV相关的DEGs、7291 个BHS相关的DEGs、7654 个BSS相关的DEGs,以及6578 个BDS相关的DEGs,其KEGG富集分析取交集后,有Janus激酶(Janus kinase, JAK)/信号转导与转录激活因子(signal transducer and activator of transcription, STAT)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK)、cAMP、细胞凋亡、胰岛素抵抗(insulin resistance, IR)、辅助性T细胞17(T helper cell 17, Th17)细胞分化等83条共同通路。JAK/STAT通路是细胞因子激活受体介导信号转导的核心,通过调控白细胞介素(interleukin, IL)-23、IL-22、IL-6等多种PV关键细胞因子表达诱导发病[14-15]。MAPK信号通路可以引发炎症反应,促进表皮过度增殖,加剧PV严重程度[16-17]。Th17细胞分化产生的IL-17、IL-22能促进角质形成细胞促炎趋化因子分泌、细胞增殖和角化过度,诱导PV发病[18-19]。IR能够直接促进角质形成细胞和成纤维细胞增殖,且IR指数与PV严重程度呈正相关[20]。以上相关研究结论与预测结果一致,表明本研究对PV生物信息学分析的结果具有科学性。为进一步探索PV不同中医证型的核心靶点,本研究将其各证型DEGs之间及PV的DEGs取交集获得重要特征基因。结果显示,MLEC、TULP3、SETD9、NEMP2、BTG3为BHS的重要特征基因,DUSP15、C1QTNF7、SLC12A5、TRIM63、UBAP1L为BSS的重要特征基因,重组小鼠蛋白(recombinant mouse protein, RRNAD1)、GTP酶激活蛋白ASAP3蛋白(ASAP3 protein, ASAP3 )、人肌间蛋白2(human myomesin 2, MYOM2)为BDS的重要特征基因。TULP3基因沉默处理后磷酸酯酶与张力蛋白同源物(phosphatase and tensin homolog, PTEN)磷酸化水平明显上调,并能负向调节磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol3-kinase, PI3K)/蛋白激酶B (protein kinase B, PKB,又称AKT)信号轴控制BHS发展[21-22]。BTG3作为抗增殖BTG基因家族的成员,可以调节STAT水平参与BHS发病[23-24]。SLC12A5影响转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β, TGF-β)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α)、IL-17及γ干扰素(interferon-γ, IFN-γ)的分泌,其中IFN-γ、TNF-α、IL-17在BSS患者中显著升高[25-26]。C1QTNF7属于C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白家族成员,可以调节葡萄糖代谢紊乱、胰岛素抵抗等病理过程。研究显示,伴有代谢紊乱的PV患者中BSS的发生率最高[27-28]。此外,细胞凋亡造成的表皮异常与BDS密切相关,RRNAD1、ASAP3能够通过控制蛋白质合成、细胞增殖及凋亡等过程,调节表皮细胞分化与增殖,干预BDS的发生[29-30]。目前未见MLEC、SETD9、NEMP2、DUSP15、TRIM63、UBAP1L、ASAP3、MYOM2参与PV及不同中医证型的报道,其相关机制仍有待进一步研究。综上,本研究筛选出的部分重要特征基因与相关研究结果基本一致,且研究结果显示,本次预测基因与PV病理机制存在一定联系,进一步证明了预测结果的可靠性。
本研究的局限性在于:①GEO数据库中纳入的PV中医证型的数据较少且数据集单一;②PV常合并代谢及心血管系统疾病等危险因素,在GSE192867数据集中相关信息欠缺,无法开展相关性研究;③本研究未对重要特征基因的诊断效能进行外部数据的验证及体、内外实验验证。今后课题组将在本研究基础上开展体内、外实验,进一步验证分析结果,深入研究各中医证型信号通路差异性,阐述不同证型的病理机制,继续研究不同证型基因间的内在联系以及在PV各个阶段的诊断价值及意义,为不同中医证型PV的临床诊疗提供科学依据。
* * *
作者贡献声明 刘学伟负责论文构思、提供资源、监督指导、初稿写作和审读与编辑写作,贾皇超和王丽云负责数据审编、正式分析和初稿写作,王子雯和许孟月负责研究方法和软件,李云飞和王茸慧负责调查研究和可视化。所有作者已经同意将文章提交给本刊,且对将要发表的版本进行最终定稿,并同意对工作的所有方面负责。
Author Contribution LIU Xuewei is responsible for conceptualization, resources, supervision, writing--original draft, and writing--review and editing. JIA Huangchao and WANG Liyun are responsible for data curation, formal analysis, and writing--original draft. WANG Ziwen and XU Mengyue are responsible for methodology and software. LI Yunfei and WANG Ronghui are responsible for investigation and visualization. All authors consented to the submission of the article to the Journal. All authors approved the final version to be published and agreed to take responsibility for all aspects of the work.
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
Declaration of Conflicting Interests All authors declare no competing interests.
-
图 1 DEGs火山图
Figure 1. The volcano map of DEGs
A, "PV.txt" file; B, "BHS.txt" file; C: "BSS.txt" file ; D, "BDS.txt" file. Each dot represents a gene, with the green dots representing down-regulated DEGs, the gray dots representing genes not differentially expressed, and the red dots representing up-regulated DEGs.
图 2 DEGs功能富集分析
Figure 2. DEGs functional enrichment analysis results
A, Bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of PV-related DEGs; B, bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of BHS-related DEGs; C, bubble map of KEGG enrichment analysis of BSS related DEGs; D, bubble diagram of KEGG enrichment analysis of BDS-related DEGs; E, Venn diagram of KEGG pathways for all DEGs; F, the intersection KEGG pathway of all DEGs.
图 4 机器学习算法筛选不同中医证型的重要特征基因
Figure 4. The key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome types were screened by machine learning algorithm
A, Box plot of BHS sample residuals, with the red dots representing the root mean square of residuals; B, importance ranking of BHS characteristic genes in the two models; C, box plot of BSS sample residuals, with the red dots representing the root mean square of residuals; D, the importance ranking of BSS characteristic genes in the two models.
图 5 不同中医证型重要特征基因诊断效能的评价
Figure 5. Evaluation of the diagnostic efficacy of key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome types
A, Chromosomal location of key characteristic genes; B-C, ROC curve of key characteristic genes in the "PV.txt" file; D, ROC curve of key BHS characteristic genes in "BHS. txt" file; E, ROC curve of key BSS characteristic genes in the "BSS.txt" file; F, ROC curve of BDS key characteristic genes in "BDS.txt" file.
图 6 重要特征基因的表达趋势
Figure 6. Expression trends of key characteristic genes
A, Box diagram of the expression of key characteristic genes of different TCM syndrome types in the "PV.txt" file; B, box diagram of the expression of BHS key characteristic genes in the "Bhs.txt" file; C, box diagram of the expression of BSS key characteristic genes in the "BSS.txt" file; D, box diagram of the expression of BDS key characteristic genes in the file "BDS.txt". * P<0.05, *** P<0.001.
-
[1] BOEHNCKE W H, SCHON M P. Psoriasis. Lancet,2015,386(9997): 983–994. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61909-7.
[2] 许孟月, 王子雯, 李建伟, 等. 冯宪章运用卫气营血截断法治疗银屑病血热证经验. 中医杂志,2021,62(11): 939–942. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.11.004. XU M Y, WANG Z W, LI J W, et al. Professor FENG Xianzhang's experience in treating psoriasis with Blood-heat Pattern using Wei-qi-ying-blood Truncation Method. J Trad Chin Med,2021,62(11): 939–942. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.11.004.
[3] 刘欣, 张广中, 肖士菊, 等. 银屑病血热证与血燥证肠道菌群特征研究. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2021,23(7): 2480–2486. doi: 10.11842/wst.20200909005. LIU X, ZHANG G Z, XIAO S J, et al. Study on characteristics of gut microbiota in Blood-Hest Syndrome and Blood-Dryness Syndrome of psoriasis. World Sci Tech Modern Trad Chin Med Mater Med,2021,23(7): 2480–2486. doi: 10.11842/wst.20200909005.
[4] 安月鹏, 杨素清, 张晴, 等. 中医药调控microRNA治疗银屑病的研究进展. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(11): 206–216. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20221196. AN Y P, YANG S Q, ZHANG Q, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment of psoriasis by regulating microRNA: a review. Chin J Exp Trad Med Form,2022,28(11): 206–216. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20221196.
[5] 杨玉洁, 郭杨, 田野, 等. 应用蛋白芯片筛选寻常型银屑病血热证和血瘀证血清差异蛋白的研究. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(10): 5251–5256. YANG Y J, GUO Y, TIAN Y, et al. Protein chip screening of serum differential proteins in psoriasis vulgaris with blood heat syndrome and blood stasis syndrome. Chin J Trad Chin Med Pharm,2020,35(10): 5251–5256.
[6] 李兴渊, 朱明军, 彭广操, 等. 基于生物信息学和机器学习的心肌梗死后心室重构关键基因的筛选. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2022,57(5): 623–631. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6825.2021.11.035. LI X Y, ZHU M J, PENG G C, et al. Screening of hub genes for ventricular remodeling post-myocardial infarction based on bioinformatics and machine learning. J Zhengzhou Univ (Med Sci),2022,57(5): 623–631. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6825.2021.11.035.
[7] 王景乐, 徐曦, 郎广平, 等. 基于生物信息学方法分析银屑病病理机制中的调节网络. 遵义医科大学学报,2023,46(2): 152–159. doi: 10.14169/j.cnki.zunyixuebao.2023.0030. WANG J L, XU X, LANG G P, et al. Analysis of regulatory network in the pathogenesis of psoriasis based on bioinformatics. J Zunyi Med Univ,2023,46(2): 152–159. doi: 10.14169/j.cnki.zunyixuebao.2023.0030.
[8] 张汝益, 杨芳, 管尤涛, 等. 生物信息学联合机器学习探究主动脉瓣膜钙化潜在的诊断标志物. 重庆医科大学学报,2023,48(12): 1493–1500. doi: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.003399. ZHANG R Y, YANG F, GUAN Y T, et al. Potential diagnostic markers for aortic valve calcification: a study based on bioinformatics and machine learning. J Chongqing Med Univ,2023,48(12): 1493–1500. doi: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.003399.
[9] 于瑜, 王钟兴. 基于生物信息学途径筛选缺血性脑卒中关键基因及药物预测. 中山大学学报(医学科学版),2021,42(1): 42–50. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci). YU Y, WANG Z X. Screening of key genes and prediction of drugs for ischemic stroke based on bioinformatics approach. J Sun Tat-sen Univ (Med Sci),2021,42(1): 42–50. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).
[10] 尚莎莎, 陈玉善, 李晓辉, 等. 动脉粥样硬化斑块破裂的关键免疫相关基因和潜在治疗药物的识别. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2022,43(4): 348–360. doi: 10.11778/j.jdxb.20220119. SHANG S S, CHEN Y S, LI X H, et al. Identification of hub immune-related genes and potential therapeutic drugs for atherosclerotic plaque rupture. J Jinan Univ (Nat Sci Med Edn),2022,43(4): 348–360. doi: 10.11778/j.jdxb.20220119.
[11] RENDON A, SCHAKEL K. Psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci,2019,20(6): 1475. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061475.
[12] 薛凯元, 杨素清, 贾丽丹, 等. 蜈蚣败毒饮联合走罐治疗斑块型银屑病(血瘀证)的疗效评价及对免疫功能的影响. 时珍国医国药,2022,33(10): 2440–2442. XUE K Y, YANG S Q, JIA L D, et al. Efficacy evaluation of centipede Baidu drink combined with walking cup in the treatment of plaque psoriasis ( blood stasis syndrome) and its influence on immune function. Lishizhen Med Materia Medica Res,2022,33(10): 2440–2442.
[13] 吕景晶, 韩晓丽, 孙雯雯, 等. 养血解毒汤联合中药药浴治疗血燥型银屑病临床观察. 中华中医药杂志,2021,36(7): 4405–4407. LYU J J, HAN X L, SUN W W, et al. Clinical observation of psoriasis of blood dryness syndrome with Yangxue Jiedu Decoction combined with traditional Chinese medicine bath therapy. Chin J Trad Chin Med Pharm,2021,36(7): 4405–4407.
[14] HOWELL M D, KUO F I, SMITH P A. Targeting the Janus kinase family in autoimmune skin diseases. Front Immunol,2019,10: 2342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02342.
[15] HU X, LI J, FU M, et al. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: from bench to clinic. Signal Transduct Target Ther,2021,6(1): 402. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00791-1.
[16] SAKURAI K, DAINICHI T, GARCET S, et al. Cutaneous p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation triggers psoriatic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol,2019,144(4): 1036–1049. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.06.019.
[17] GUO H, LI M, LIU H. Selenium-rich yeast peptide fraction ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice by inhibiting inflammation via MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(4): 2112. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042112.
[18] HAWKES J E, YAN B Y, CHAN T C, et al. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway and the treatment of psoriasis. J Immunol,2018,201(6): 1605–1613. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800013.
[19] HU Y, ZHU Y, LIAN N, et al. Metabolic syndrome and skin diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2019,10: 788. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00788.
[20] POLIC M V, MISKULIN M, SMOLIC M, et al. Psoriasis severity-a risk factor of insulin resistance independent of metabolic syndrome. Int J Environ Res Public Health,2018,15(7): 1486. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15071486.
[21] SONG J, FU Q, LIU G, et al. TULP3 silencing suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in gastric cancer via the PTEN/Akt/Snail pathway. Cancer Treat Res Commun,2022,31: 100551. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2022.100551.
[22] HADDADI N, LIN Y, TRAVIS G, et al. PTEN/PTENP1: “Regulating the regulator of RTK-dependent PI3K/Akt signalling”, new targets for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer,2018,17(1): 37. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0803-3.
[23] ENG Z H, ABDULLAH M I, NG K L, et al. Whole-exome sequencing and bioinformatic analyses revealed differences in gene mutation profiles in papillary thyroid cancer patients with and without benign thyroid goitre background. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2023,4(13): 1039494. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1039494.
[24] 齐潇丽, 李莹, 蒋俊青, 等. 清热凉血方对咪喹莫特诱导的银屑病样小鼠模型JAKs/STATs通路表达影响的研究. 中国中西医结合皮肤性病学杂志,2021,20(2): 162–166. QI X L, LI Y, JIANG J Q, et al. Effects of Clearing Heat and Cooling Blood Recipe on JAKs/STATs Pathway Expression in Psoriasis-like Mice Models Induced by Imiquimod. Chin J Dermato Venerol Integ Trad W Med,2021,20(2): 162–166.
[25] FUKUDA A, WATANABE M. Pathogenic potential of human SLC12A5 variants causing KCC2 dysfunction. Brain Res,2019,1710: 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.12.025.
[26] 李明路, 郭晓莉, 于亚明, 等. 解毒化瘀汤联合刺络放血疗法对血瘀热结证寻常型银屑病患者血清炎性因子及CREB信号传导通路相关蛋白表达的影响. 现代生物医学进展,2023,23(3): 579–583. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2023.03.036. LI M L, GUO X L, YU Y M, et al. Effect of Jiedu Huayu Decoction combined with Blood Letting Puncture Therapy on the expression of serum inflammatory factors and CREB signal transduction pathway related proteins in patients with psoriasis vulgaris of Blood Stasis Heat Stagnation Syndrome. Prog Modn Biomed,2023,23(3): 579–583. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2023.03.036.
[27] LI K, LIANG Z, XU W, et al. CTRP7 is a biomarker related to insulin resistance and oxidative stress: cross-sectional and intervention studies in vivo and in vitro. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2022,2022: 6877609. doi: 10.1155/2022/6877609.
[28] SUN X, ZHAO H, WANG R, et al. Psoriasis complicated with metabolic disorder is associated with traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types: a hospital-based retrospective case-control study. Curr Med Res Opin,2022,11: 1–7. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2022.2129803.
[29] GUO L, FU J, SUN S, et al. MicroRNA-143-3p inhibits colorectal cancer metastases by targeting ITGA6 and ASAP3. Cancer Sci,2019,110(2): 805–816. doi: 10.1111/cas.13910.
[30] IZZI B, NORO F, CLUDTS K, et al. Cell-specific PEAR1 methylation studies reveal a locus that coordinates expression of multiple genes. Int J Mol Sci,2018,19(4): 1069. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041069.

开放获取 本文遵循知识共享署名—非商业性使用4.0国际许可协议(CC BY-NC 4.0),允许第三方对本刊发表的论文自由共享(即在任何媒介以任何形式复制、发行原文)、演绎(即修改、转换或以原文为基础进行创作),必须给出适当的署名,提供指向本文许可协议的链接,同时标明是否对原文作了修改;不得将本文用于商业目的。CC BY-NC 4.0许可协议详情请访问 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0

 首页
首页


 下载:
下载: